一维数组
存储结构
$\text{Loc}(a[i]) = \text{Loc}(a[0]) + i\times L$
- $L$——每个元素的存储空间
二维数组
存储方式
行优先
$\text{Loc} (a[i][j])=\text{Loc}(a[0][0])+(i\times n+j)\times L$
列优先
$\text{Loc} (a[i][j])=\text{Loc}(a[0][0])+(j\times m+i)\times k$
矩阵
特殊矩阵
对称矩阵
行优先
$\text{Index} (a[i][j])=\left\{\begin{array}{**lr**} \dfrac{i(i+1)}{2}+j , j{\leq}i ,下三角矩阵& \\{\dfrac{j(j+1)}{2}}+i,j{\leq}i,上三角矩阵\end{array} \right. $三角矩阵
上三角
$k=\left\{ \begin{array}{l} \dfrac{i\left( i+1 \right)}{2}+j\ \ i\ge j\\ \dfrac{n\left( n+1 \right)}{2}\ \ \ \ \ \ i三对角矩阵
$$ \left[ \begin{matrix}{} a_{1,1}& a_{1,2}& & & & \\ a_{2,1}& a_{2,2}& a_{2,3}& & 0& \\ & a_{3,2}& a_{3,3}& a_{3,4}& & \\ & & \ddots& \ddots& \ddots& \\ & 0& & a_{n-1,n-2}& a_{n-1,n-1}& a_{n-1,n}\\ & & & & a_{n,n-1}& a_{n,n}\\ \end{matrix} \right] $$存储位置:$k=2i+j-3 $
矩阵位置:$\left\{ \begin{array}{l} i=\dfrac{k+1}{3}+1\\ j=k-2i+3\\ \end{array} \right. $
稀疏矩阵
存储结构
三元组
以三元组$<i,j,a_{ij}>$表示
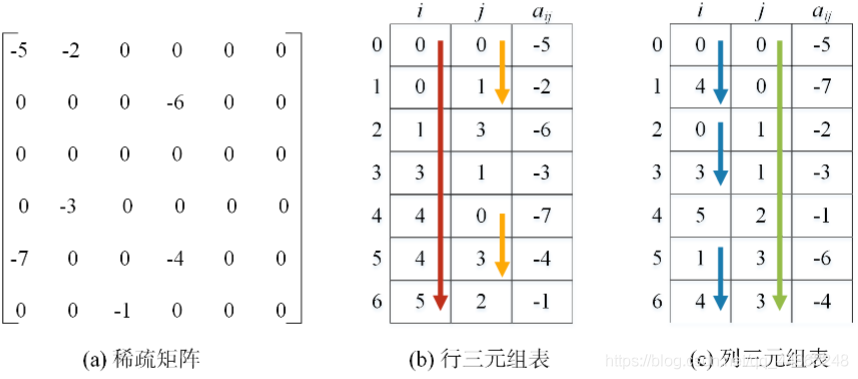
定义
typedef struct term
{
int col,row; // 列下标,行下标
ElemType value; // 非零值
}Term;
typedef struct sparsematrix
{
int m,n,t;
Term table[maxSize]; // 存储非零元的三元组表
}邻接表
十字链表
转置算法
算法一
交换$i,j$
以$i,j$从小到大排序
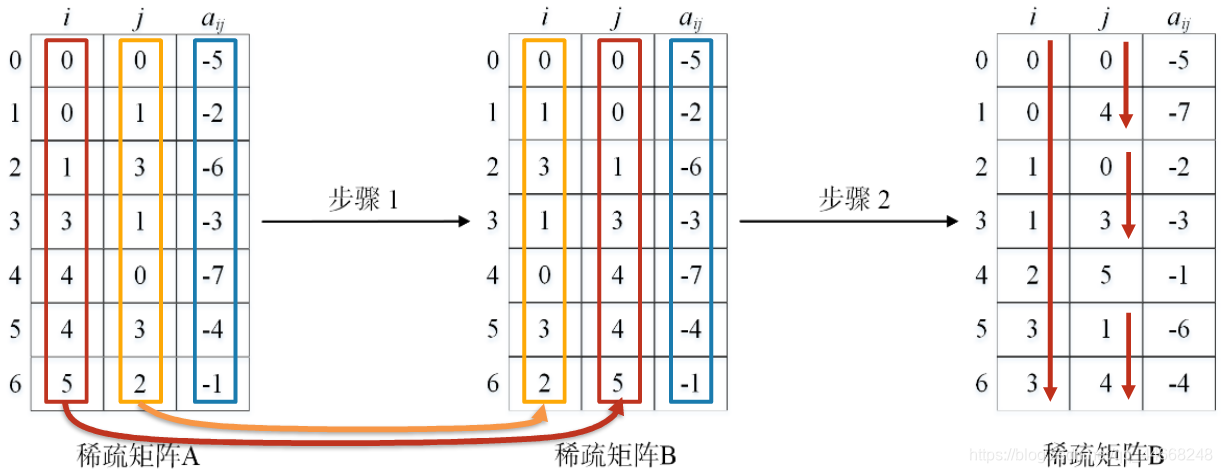
时间复杂度
步骤一:$O(t)$
$t$——非零元素个数
排序复杂度
算法二
- 找到所有$<i,0,a_{i0}>$,交换$i,j$后依次保存到稀疏矩阵$B$
- 找到所有$<i,1,a_{i1}>$,交换$i,j$后依次保存到稀疏矩阵$B$
- $……$
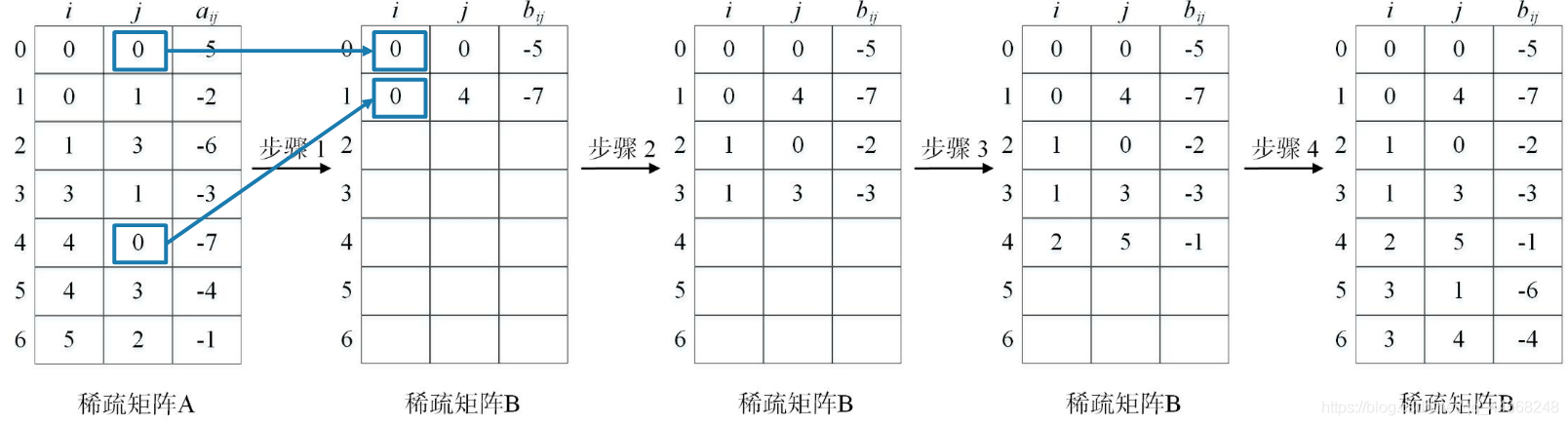
时间复杂度
$O(nt)$
- $t$——非零元素个数
- n——列数
快速转置算法
计算每列非零元素个数$num$
计算前$j$列非零元素个数$k$
$k[j]=\left\{\begin{array}{**lr**} 0 , j=0 & \\k[j-1]+num[j-1],j>0\end{array} \right. $0 1 2 3 4 num 2 1 2 2 0 k 0 2 3 5 7 从原数组每列开始,放于其$k[j]$位置
$k++$
$i,j$互换
广义表
广义表长度:表最外层元素个数
广义表深度:括号最大层数
表头 & 表尾:广义表非空时,首个元素为表头;其余元素组成的广义表为表尾
存储结构
头尾链表存储结构
广义表结点
| 结点类型:1 | link指向原子结点 | next指向下一个广义表结点 |
原子结点
| 结点类型:0 | data |
扩展线性表存储结构
头结点
| 1 | NULL | next |
子表结点
| 1 | 指向表内元素 | next |
原子结点
| 0 | data | next |
串
存储结构
定长存储
typedef struct{
char str[maxSize + 1];
int length;
}Str;变长存储结构
typedef struct{
char *ch;
int length;
}Str;新建串
Str S;
S.length = L;
S.ch = (char*)malloc((L+1) * sizeof(char)); // L+1包括'\0'基本操作
赋值
int strAssign(Str& str, char* ch){
if(str.ch) // 如串已经指向一片存储空间,则先释放
free(str.ch);
char *c = ch; // c指向连续空间的首地址
int len = 0; // ch长度,初始化0
while(*c){ // 遍历ch
++len; // 长度++
++c; // ch遍历
}
if(len == 0){ // 空串
str.ch = NULL;
str.lenth = 0;
return 1;
}else{
str.ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len+1)); // 分配空间
if(str.ch == NULL) // 分配失败,ch为NULL
return 0;
else{
c = ch; // c指向ch首字符
for(int i = 0 ; i <= len ; ++i, ++c) // 循环赋值
str.ch[i] = *c;
str.length = len;
return 1;
}
}
}取长
int strLength(Str str)
return str.length;比较
int strCompare(Str s1, Str s2){
for(int i = 0 ; i < s1.length && i < s2.length ; ++i) // 扫描较短字符串
if(s1.ch[i] != s2.ch[i])
return (s1.ch[i] - s2.ch[i]);
return (s1.length - s2.length);
} 串连接
int concat(Str& str, Str str1, Str str2){
if(str.ch){ // 若不为空
free(str.ch); // 释放空间
str.ch = NULL;
}
str.ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (str1.length + str.length + 1)); // 申请空间
if(!str.ch) // 申请失败
return 0;
int i = 0;
while(i < str1.length){
str.ch[i] = str1.ch[i];
++i;
}
int j = 0;
while(j <= str2.length){
str.ch[i+j] = str2.ch[j];
++j;
}
str.length = str1.length + str2.length;
return 1;
} 求子串
int getSubString(Str& substr, Str str, int pos, int len){ // str中取一个pos为起点,长为len的子串
if(pos < 0 || pos >= str.length || len < 0 || len > str.length - pos) // 越界
return 0;
if(substr.ch){ // 清空
free(substr.ch)
substr.ch = NULL;
}
if(len == 0){ // 空串
substr.ch = NULL
substr.length = 0;
return 1;
}else{
substr.ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len+1)); // 分配空间
int i = pos, j = 0;
while(i < pos + len){
substr.ch[j] = str.ch[i];
++i;
++j;
}
}
substr.length = len;
return 1;
}清空
int claerString(Str& str){
if(str.ch){
free(str.ch);
str.ch = NULL;
}
str.length = 0;
return 1;
}KMP算法
next数组
- 公共长度为$n$,则从$n+1$位开始比较
- 若
next[j]=t- 若
P[j]=P[t],则next[j+1]=t+1 - 若
P[j]≠P[t],则循环将t赋值为next[t],直到t=0或满足上述上述为止 - 当
t=0时,next[j+1]=1
- 若
void getNext(Str substr, int next[]){
int j = 1, t = 0;
next[1] = 0; // next[1] 赋值0
while(j < substr.length){ // 在模式串长度内
if(t = 0 || substr.ch[j] == substr.ch[t]){ // j位置和t位置相等时
next[j+1] = t + 1;
++t;
++j;
}else // next赋值给t
t = next[t];
}
}KMP代码
/*KMP算法
str:主字符串
substr:模式串
next:next数组
*/
int KMP(Str str, Str substr, int next[]){
int i = 1, j = 1;
while(i <= str.length && j <= substr.length){ // 越界
if(j == 0 || str.ch[i] == substr.ch[j]){ // j为0 ij相等
++i;
++j;
}else{
j = next[j]; // next指明下一个比较的位置
}
}
if(j > substr.length)
return (i - substr.length);
else
return 0;
}Nextval
void getNextval(Str substr,int nextval[], int next[]){
int j = 1, t = 0;
next[1] = 0; // next[1] 赋值0
nextval[1] = 0;
while(j < substr.length){ // 在模式串长度内
if(t = 0 || substr.ch[j] == substr.ch[t]){ // j位置和t位置相等时
if(substr.ch[j+1] != substr.ch[t+1])
nextval[j+1] = t+1;
else
nextval[j+1] = nextval[t+1];
++t;
++j;
}else // next赋值给t
t = nextval[t];
}
}


